If one looks only at the flow side of the equation, it's
difficult to see what the problem might be. The ordering of
the elements of the flow is preserved in the area tree, and
where elements are in an hierarchical relationship in the
flow, they will generally be in an hierarchical relationship
in the area tree. In such circumstances, the recursive
processing of the flow seems quite natural.
The problem becomes more obvious when one thinks about the
imposition of an unrelated page structure over the
hierarchical structure of the document content. Take, e.g.,
the processing of a nested flow structure which, at a certain
point, is scanning text and generating line-areas, nested
within other block areas and possibly other line areas. The
page fills in the middle of this process. Processing at the
lowest level in the tree must now suspend, immediately
following the production of the line-area which filled the
page. This same event, however, must also trigger the closing
and flushing to the area tree of every open area of which the last
line-area was a descendant.
Once all of these areas have been closed, some dormant process
or processes must wake up, flush the area sub-tree
representing the page, and open a new page sub-tree in the
area tree. Then the whole nested structure of flow objects
and area production must be re-activated, at the point in
processing at which the areas of the previous page were
finalised, but with the new page environment. The most
natural way of expressing the temporal relationship of these
processes is by means of co-routines.
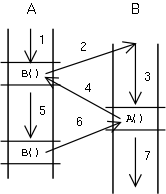
Normal sub-routines (methods) display a hierarchical
relationship where process A suspends on invoking process B,
which on termination returns control to A which resumes from
the point of suspension. Co-routines instead have a parallel
relationship. Process A suspends on invoking process B, but
process B also suspends on returning control to process A. To
process B, this return of control appears to be an invocation
of process A. When process A subsequently invokes B and
suspends, B behaves as though its previous invocation of A has
returned, and it resumes from the point of that invocation.
So control bounces between the two, each one resuming where it
left off.
Figure 1
For example, think of a page-production method working on a
complex page-sequence-master.
 |  |  |
 |
void makePages(...) {
...
while (pageSequence.hasNext()) {
...
page = generateNextPage(...);
boolean over = flow.fillPage(page);
if (over) return;
}
}
|  |
 |  |  |
The fillPage() method, when it fills a page, will
have unfinished business with the flow, which it will want to
resume at the next call; hence co-routines. One way to
implement them in Java is by threads synchronised on some
common argument-passing object.

