
|



















|
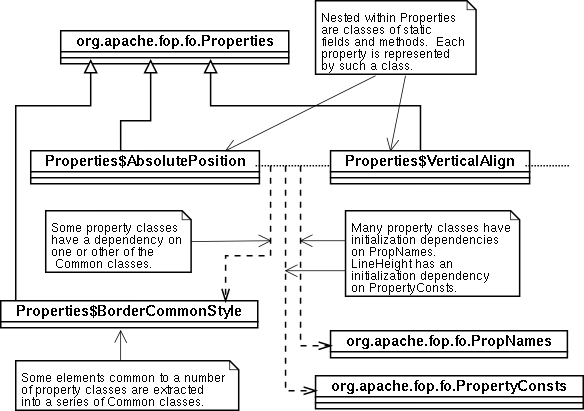
 |  |  |  |  fo.Properties and the nested properties classes fo.Properties and the nested properties classes |  |  |  |  |
|
|
Given the intention that individual properties have only a
virtual instantiation in the arrays of
PropertyConsts, these classes are intended to
remain as repositories of static data and methods. The name
of each property is entered in the
PropNames.propertyNames array of
Strings, and each has a unique integer constant
defined, corresponding to the offset of the property name in
that array.
 |  |  |  |  Fields common to all classes Fields common to all classes |  |  |  |  |
final int dataTypes -
This field defines the allowable data types which may be
assigned to the property. The value is chosen from the
data type constants defined in Properties, and
may consist of more than one of those constants,
bit-ORed together.
final int traitMapping -
This field defines the mapping of properties to traits
in the Area tree. The value is chosen from the
trait mapping constants defined in Properties,
and may consist of more than one of those constants,
bit-ORed together.
final int initialValueType -
This field defines the data type of the initial value
assigned to the property. The value is chosen from the
initial value type constants defined in
Properties.
final int inherited -
This field defines the kind of inheritance applicable to
the property. The value is chosen from the inheritance
constants defined in Properties.
|
 |  |  |  |  Datatype dependent fields Datatype dependent fields |  |  |  |  |
Enumeration types -
final String[] enums
This array contains the NCName text
values of the enumeration. In the current
implementation, it always contains a null value at
enum[0].
final String[]
enumValues
When the number of
enumeration values is small,
enumValues is a reference to the
enums array.
final HashMap
enumValues
When the number of
enumeration values is larger,
enumValues is a
HashMap statically initialized to
contain the integer constant values corresponding to
each text value, indexed by the text
value.
final int
enumeration-constants
A
unique integer constant is defined for each of the
possible enumeration values.
Many types:
final datatype
initialValue -
When the initial datatype does not have an implicit
initial value (as, for example, does type
AUTO) the initial value for the property is
assigned to this field. The type of this field will
vary according to the initialValueType
field.
AUTO: PropertyValueList auto(property,
list)> -
When AUTO is a legal value type, the
auto() method must be defined in the property
class.
NOT YET IMPLEMENTED.
COMPLEX: PropertyValueList complex(property,
list)> -
COMPLEX is specified as a value type when complex
conditions apply to the selection of a value type, or
when lists of values are acceptable. To process and
validate such a property value assignment, the
complex() method must be defined in the
property class.
|
|
Previous: property classes overview.
|
|
|

